Information architecture
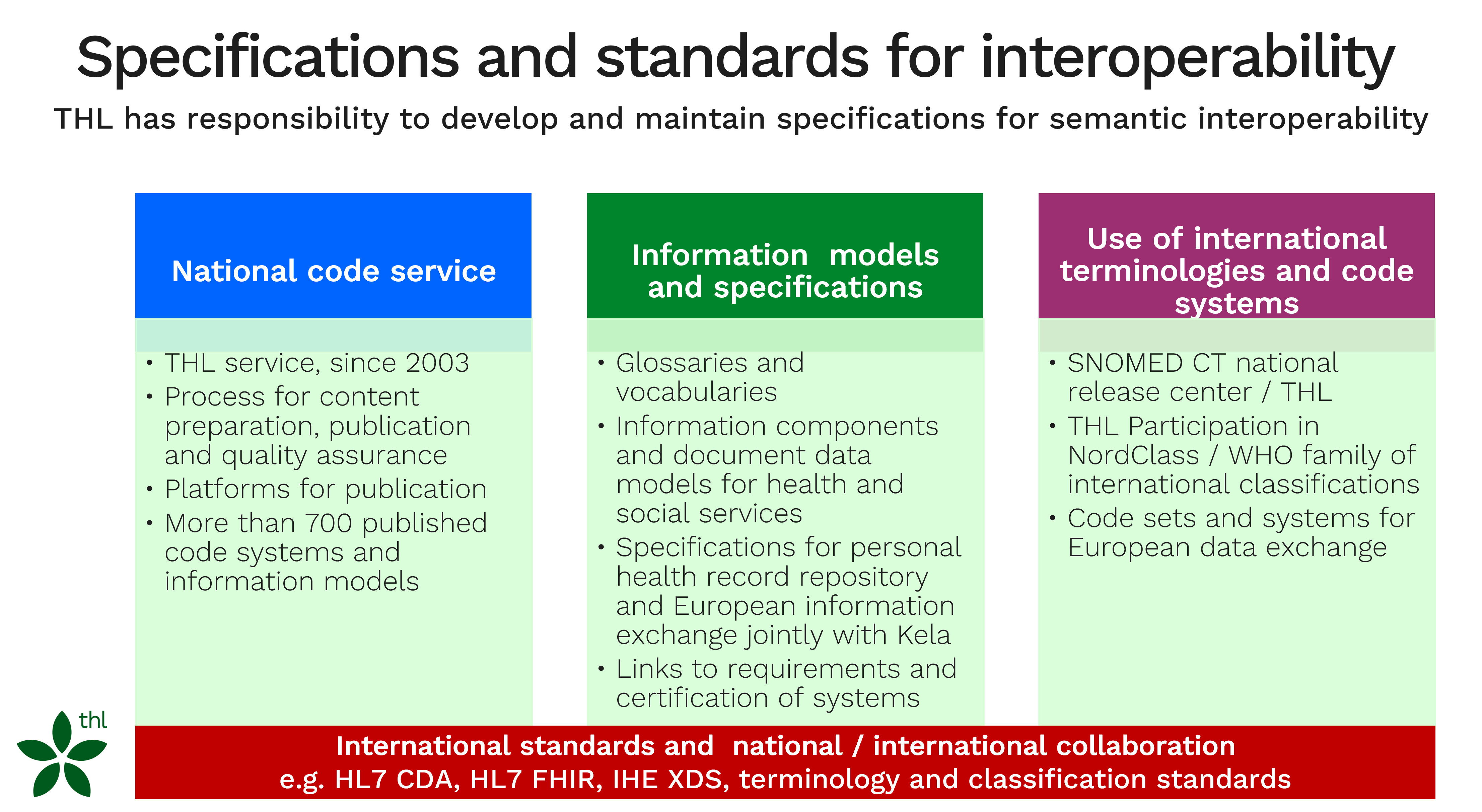
In Finland, the national information architecture for social welfare and healthcare leans on nationally interoperable information models and specifications. It is mandatory to use them in patient and client information systems. THL's legal task is to ensure the quality of the data structures used in social welfare and health care, and to develop, maintain and publish them.
The national information specifications include glossaries and vocabularies, information components and document data structures for health and social services, as well as classifications and code systems. When necessary, international terminologies and code systems are adapted nationally. International standards and models form the basis for many of the codes and data structures.
Developing information architecture with a broad network
It is highly important to take account the different viewpoints. We work closely with the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health (STM), the Social Insurance Institution of Finland (Kela), information systems developers, as well as social welfare and health care actors, when developing the national level information models and structures.
All information models and specifications undergo a careful preparation process to ensure the quality and interoperability. The development of the information architecture is based on existing strategies and national development plans.
Code Service
The purpose of the Code Service is to publish the nationally coherent data structures needed by social and health care client and patient information systems. The Code Service activities takes care of the quality, development and maintenance of data structures. The publication of data structures is subject to an administrative decision.
THL National Code Service publishes the national codes, classifications, document structures and data components. Four platforms are used to distribution:
- National Code Server (codes and classifications for social and health care in Finnish and Swedish)
- Sosmeta (social care document structures and metadata service in Finnish and Swedish)
- Termeta (healthcare document structures and metadata service in Finnish and Swedish)
- Sote-sanastot (glossary of information management in social and health care in Finnish and Swedish)
The distribution services are free of charge. Client and patient information systems can be connected to the code server in such a way that updates are almost automatic.
Vocabulary work
The primary objective of vocabulary work related to information management in social and health care is to define the key concepts used in client and patient information systems. The harmonisation and standardisation of the terminology is also part of this work. Harmonised concepts and terms are also essential for documenting client and patient data and for collecting statistical and register data. That is, to enable once documented data to be used in secondary use.
The vocabularies will be used for example in regulations, guidelines, specifications, training and communication materials related to Kanta services.
THL also actively participates in international vocabulary cooperation.
International cooperation
We also actively promote international information architecture development.
The development of international classifications in the field of health care involves the definition of key concepts and the development of terminology recommendations in Finnish.
European projects will promote the development and deployment of cross-border digital health services. THL is involved in projects such as defining classifications and codes for the data content of electronic prescriptions together with the EU Commission and other Member States.
THL promotes the introduction of the international SNOMED CT framework in Finland and organises national translation work.
Preparations for the introduction of the ICD-11 diagnostic classification will be made between 2023 and 2026. THL will promote the implementation in cooperation with health professionals, organisations, information system providers and other stakeholders.




