Finnish tobacco control policy and legislation
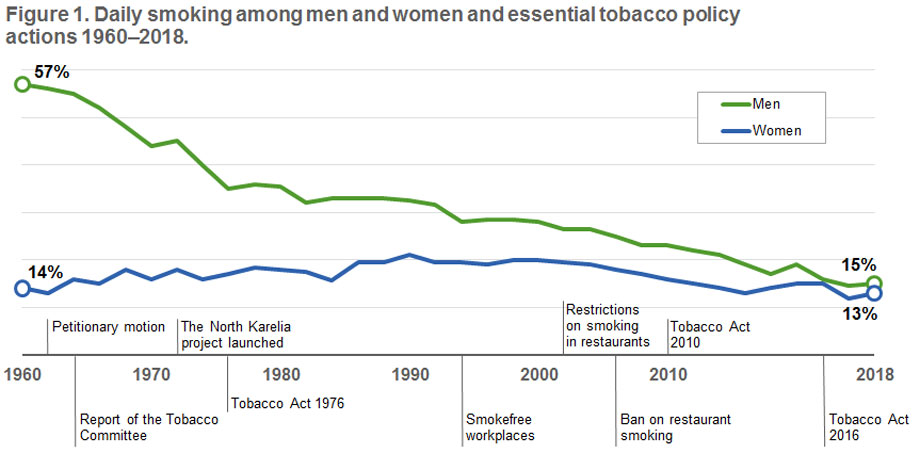
Finland has been among the world’s pioneer countries in tobacco policy since 1976, when the Tobacco Act introduced measures to reduce the use of tobacco products. The Tobacco Act came into force in 1977 and has been revised several times since then (see Figure 1).
The objective of the Tobacco Act
A few of the implemented central measures of the Tobacco Act over the years have been
- smoke-free workplaces (in the mid-1990s)
- bans of restaurant smoking (in 2009)
- a point-of-sale display and advertising ban (in 2012)
In 2010, the aim to end the use of tobacco (the endgame) became the objective of the Tobacco Act. The objective was broadened in 2016 to include the use of all tobacco and nicotine products under the Tobacco Act (excluding the use of nicotine replacement therapy products, regulated under the Medicines Act). The objective is considered met if no more than 5% of the population uses tobacco or nicotine products daily by 2030.
The 2016 flavour ban on tobacco and nicotine products
In 2016, the Tobacco Act was harmonised with the EU Tobacco Products Directive (2014/40/EU) with additional national regulations. Electronic nicotine and non-nicotine delivery devices, and e-liquids started to be regulated under the Tobacco Act. An important measure for protecting youth from nicotine addiction was the ban on flavour e-liquids. All flavours are included in the ban, excluding tobacco flavourings.
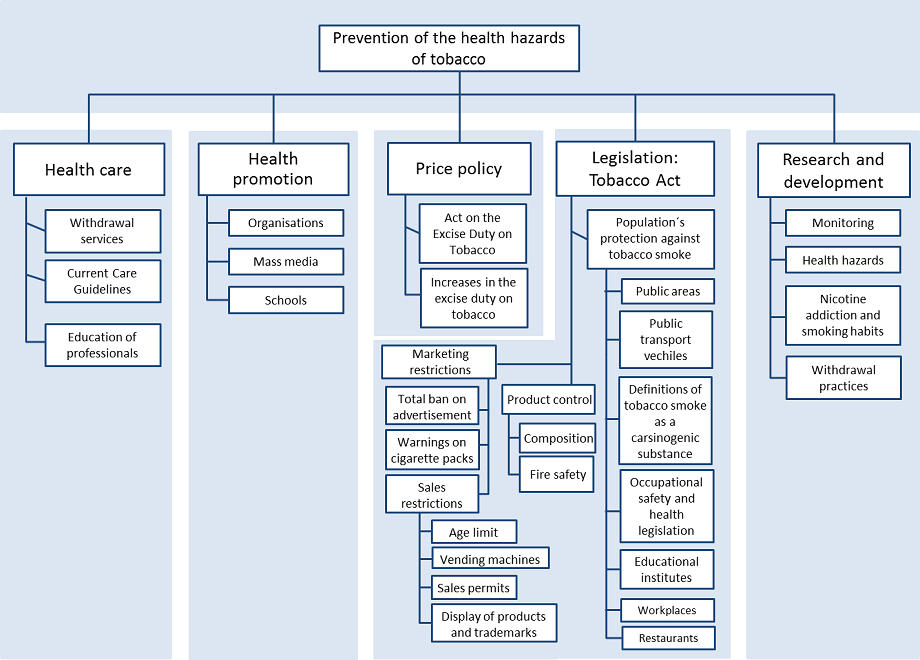
Four different measures of tobacco control policy
The central areas and measures for implementing tobacco policy are
- health education
- price policy
- restrictions
- research and development
All of these areas have later been supplemented after the enactment of the Tobacco Act, but the basic configuration has remained more or less the same as it was originally.
Figure 2. Measures and areas of Finland’s health-oriented tobacco policy.
Click to open picture in full size (pdf 120 kB)
The Tobacco Act's regulations are overseen by the National Supervisory Authority for Welfare and Health (Valvira).
Read more of the Finnish tobacco control and the Tobacco Act
Finnish Ministry of Social Affairs and Health
Read more of the tobacco taxation in Finland
European Commission
Read more of the supervision of the Finnish Tobacco Control Act
National Supervisory Authority for Welfare and Health
National Supervisory Authority for Welfare and Health (Valvira)
Valvira supervises the composition, quality control, testing laboratories, and the sale and advertising of tobacco products.